Solve Thermal Challenges: Flexible Thermally Conductive Insulating Film
Electronics are hotter than ever. Devices are getting smaller, faster, and jam-packed with power-hungry components that throw off more heat than a summer asphalt. That’s where the flexible thermally conductive insulating film comes in: low-key genius material that cools things down without frying your circuits.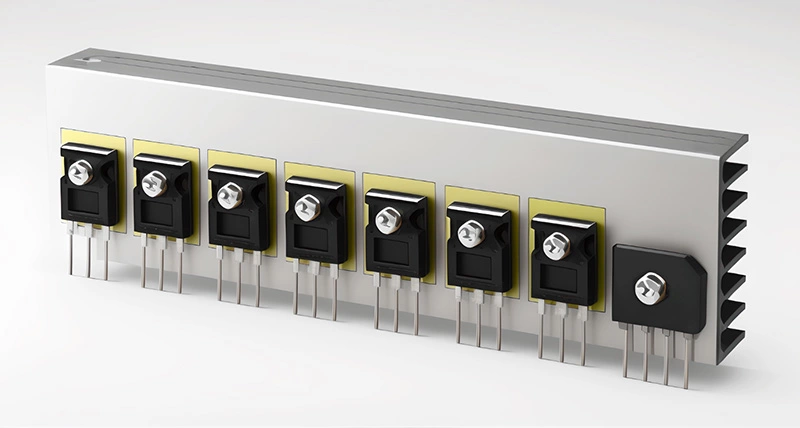
“Buyers want two things,” says Lena Wu, senior materials engineer at Sheen Electronic Technology (2024 Q1 Supplier Brief). “Thermal efficiency and electrical safety—and they want both at scale.” No compromise, no drama. Just performance that sticks through pressure and heat.
Understanding Thermal Management Challenges in Electronics
Keeping electronics cool, tough, and safe is harder than it looks—especially when things heat up or get zapped. Here's what really matters.The impact of high thermal conductivity value on performance
When your device starts cooking, thermal conductivity becomes your best friend. Materials with high heat dissipation help keep internal temps under control, which means:- Better performance optimization across longer operating hours.
- Reduced risk of system failure due to overheating.
- More stable power output even under heavy loads.
Addressing mechanical strength property in varied environments
Toughness isn't just about brute force—it’s about surviving the real world: drops, shakes, and all kinds of weather drama. For materials used in electronics:Mechanical Strength Factors:
- Durability against physical wear.
- Resistance to environmental stress like UV rays or moisture.
- Flexibility that prevents cracking during movement.
- Solid impact resistance, especially during transport.
- Withstand vibration without losing structural integrity.
In automotive systems or outdoor telecom gear? Those films take hits and keep ticking.
How dielectric strength standards influence design choices
Designers don’t get to wing it—they’ve got to meet strict safety rules around dielectric strength to avoid short circuits or worse. Here’s how those standards shape their decisions:- Minimum required breakdown voltage determines how thick insulation needs to be.
- Higher voltage applications push for materials with stronger electrical insulation properties.
- Choosing films that balance both insulation and heat transfer is tricky—but necessary.
- Safety-first thinking leads to smarter layouts that prevent arc faults and accidental discharge.
When you're juggling voltage limits and thermal loads, smart material selection isn't optional—it's survival engineering 101.
Top Applications for Flexible Thermally Conductive Films
From cutting-edge computing gear to electric rides and LED lighting, flexible thermally conductive insulating film is showing up everywhere heat needs managing smartly.Integrated circuit packaging for improved heat dissipation
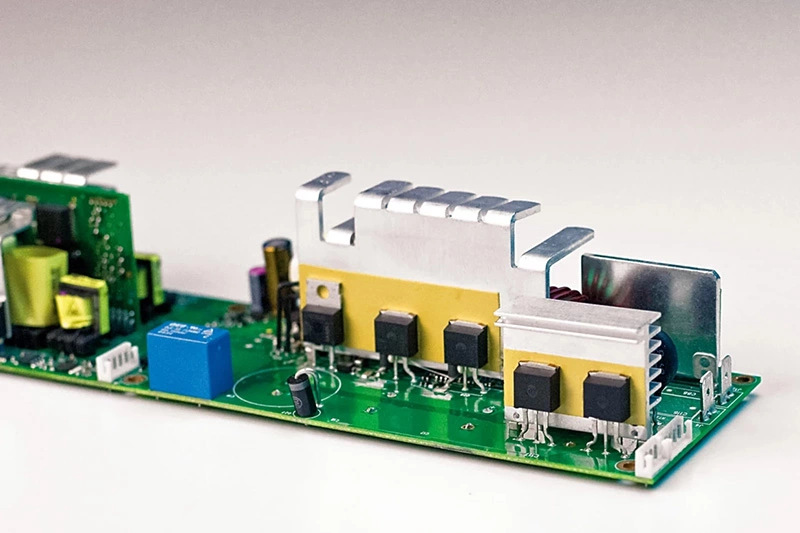
- Integrated circuits are packed tighter than ever—meaning more heat in less space. That’s where this stuff comes in handy.
- It slips between layers during semiconductor packaging, acting like a mini heat highway without adding bulk or stiffness.
LED thermal management: Maximizing efficiency with flexible films
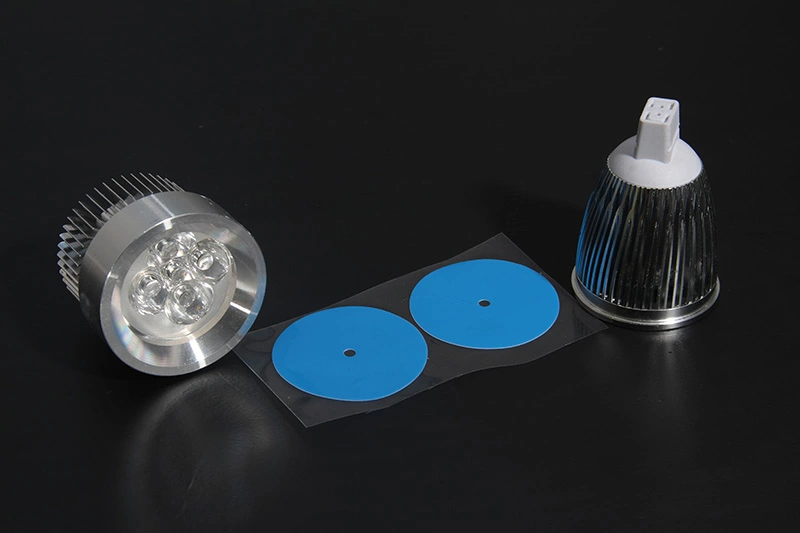

- LEDs generate less heat than bulbs—but that doesn’t mean they don’t need cooling.
- When junction temps rise, brightness drops and lifespan shrinks.
- Enter the flexible thermal film: thin, bendy, and killer at pulling heat away from the diode fast.
Electric vehicle battery packs: Thermal regulation requirements
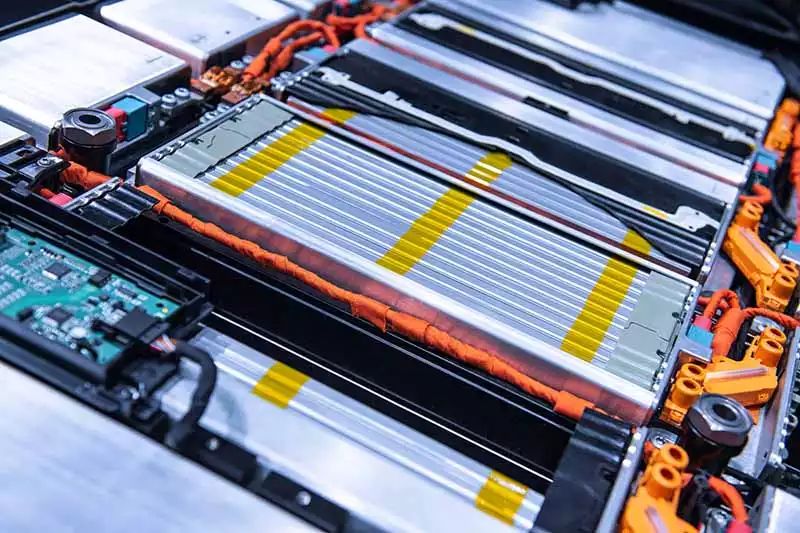

★ EVs run hot when pushed—and batteries hate the heat.
★ With lithium-ion chemistry packed tight inside those cells, poor cooling can trigger thermal runaway.
★ A thin layer of flexible insulating film helps spread and dissipate energy evenly across battery modules while maintaining strong electrical isolation.
This combo makes it ideal for use inside modern Battery Management Systems (BMS) where space is tight and safety is non-negotiable.
| Application Zone | Max Temp Tolerance | Film Thickness Range | Thermal Conductivity |
| Cell-to-cell gap | Up to 120°C | <0.5 mm | >2 W/m·K |
| Module casing | Up to 150°C | ~0.8 mm | ~3 W/m·K |
| BMS interface | Up to 100°C | <0.3 mm | ~2 W/m·K |
High-performance computing devices and their cooling challenges
In HPC environments—where processors hum nonstop—the challenge isn’t generating power; it’s getting rid of waste heat before performance tanks.Breakdown:
- CPUs and GPUs now push over 300W per chip, creating intense localized hotspots.
- Traditional metal heatsinks can’t always reach into tight server arrays or odd geometries.
- That’s where these advanced films shine: they flex around components while conducting heat laterally toward larger sinks or active coolers.
Summary Table of Key Applications & Benefits
Here’s how this material stacks up across different industries:| Application Area | Primary Benefit | Key Requirement Met |
| IC Packaging | Compact thermal spreading | Thinness + electrical insulation |
| LED Lighting | Longer lifespan via better cooling | Flexibility + high conductivity |
| EV Battery Packs | Safety through temperature control | Flame retardance + dielectric strength |
| HPC Devices/Data Centers | Maintains performance under heavy loads | Conformability + thermal transfer speed |
These films aren’t just filler—they’re foundational tools shaping how we handle modern electronics’ most pressing issue: staying cool under pressure.
5 Key Factors in Thermal Management for Electronics
Keeping electronics cool isn’t just smart—it’s survival. Here’s what really counts when managing heat in high-power devices.Material types: Influence of thermally conductive polymers
.webp)
.webp)
| Properties | Substrate Type | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
Tensile Strength (psi) |
Standard Hardness (Shore A) |
Custom Thickness (mm) |
Operating Temp (℃) |
breakdown Voltage (kV@AC) |
| SC800FG | Fiberglass | 0.8 | 450 | 90 | 0.15~1.0 | -50~200 | >4 |
| SC900FG | Fiberglass | 2.0 | 450 | 90 | 0.15~1.0 | -50~200 | >4 |
| SC1000FG | Fiberglass | 3.5 | - | 90 | 0.2~0.5 | -50~200 | >4 |
| SC2000FG | Fiberglass | 5.0 | - | 90 | 0.2~0.5 | -50~200 | >4 |
| SC800-PI-2-K4 | Polyimide | 0.9 | - | 90 | 0.1~0.5 | -50~200 | >4 |
| SC800-PI-2-K6 | Polyimide | 1.1 | - | 90 | 0.1~0.5 | -50~200 | >4 |
| SC800-PI-2-K10 | Polyimide | 1.3 | - | 90 | 0.1~0.5 | -50~200 | >4 |
- Thermally conductive polymers are changing the game by blending solid heat performance with electrical insulation.
- These materials often use polymer composites like silicone or epoxy loaded with ceramic fillers.
- They’re lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easier to mold into complex shapes than metals.
- Applications using thermal interface materials benefit from improved heat dissipation, especially when paired with precise surface control.
Application type considerations: Power electronic components
Let’s break it down:- Devices like IGBT modules and high-performance MOSFETs generate serious heat that can fry circuits if unmanaged.
- Effective cooling is critical—think custom-designed fins, optimized airflow, or embedded phase-change materials.
- Reliable thermal management prevents failures like thermal runaway, especially in compact systems with high watt loads.
Specification targets: Ensuring controlled surface roughness parameters
✔ Fine-tuned surface finish = better thermal contact.✔ Lowered thermal contact resistance = less wasted energy.
✔ Enhanced bonding = longer-lasting assemblies.
Maintaining optimal micro-texture on contact surfaces ensures that your cooling solutions actually work as planned.
A well-prepped surface improves adhesion between layers of the assembly—vital for applications using thin-film insulators like a layered polymer-based film with dielectric properties.
Process integration: Importance of precise mixing and blending
Getting the mix right isn’t just technical—it’s critical:- Uniform dispersion of fillers ensures consistent thermal conductivity.
- Controlled rheology supports smooth coating processes.
- Poor mixing leads to hotspots, weak spots, and uneven performance.
Supplier networks: The role of advanced materials providers
Here’s how top-tier suppliers support innovation:- Offer access to cutting-edge formulations tailored for specific heat transfer goals.
- Provide deep expertise in sourcing rare additives used in high-performance blends.
- Maintain strict quality assurance protocols across global supply chains.
| Supplier Type | Material Focus | Support Level | Industry Examples |
| Specialized Manufacturers | Ceramic-loaded polymers | High customization | Automotive electronics |
| Innovation Partners | Graphene-enhanced composites | R&D collaboration | Wearable tech |
| Global Distributors | Broad-spectrum TIMs | Logistics & QA support | Data center cooling |
Working with the right supplier isn’t just about getting material—it’s about securing reliability at scale. And if you're prototyping something like a multi-layered flexible thermally conductive insulating film? You’ll want someone who knows their way around both chemistry and compliance standards.
How Flexible Thermally Conductive Insulating Films Improve Efficiency
These films are game-changers for electronics, combining heat transfer with electrical insulation. Here's how they hold up under pressure and deliver consistent performance.Achieving stable chemical resistance quality in demanding applications
- Chemical resistance is crucial when devices are exposed to solvents, oils, or extreme pH levels.
- In harsh settings like automotive engine bays or industrial control units, material degradation can cause real headaches—unless the film resists it.
- Stability over time means fewer replacements, less downtime, and a more reliable product lifecycle.
- Electronics used in aerospace must endure exposure to jet fuel and hydraulic fluids—without breaking down.
- Medical equipment needs insulation that won’t degrade after repeated sterilization cycles.
- Consumer wearables often face sweat and skin contact; their internal layers must resist corrosive agents.
With Sheen Electronic Technology’s advanced formulation, these films offer proven protection against aggressive environments without sacrificing thermal performance—an edge that today’s high-efficiency systems demand.
The role of controlled temperature curing for consistency
- Controlled curing locks in uniform material properties across large production batches.
- Without precise temperature management, you risk uneven polymerization—and that leads to weak spots or inconsistent thicknesses.
- Consistency here means every roll performs like the last one—no surprises on the assembly line.
This kind of production repeatability is what manufacturers crave because it avoids waste and rework. When each batch behaves the same way during lamination or die-cutting, productivity soars—and so does confidence in final product quality.
By ensuring tight control over every degree during processing, Sheen Electronic Technology delivers high-performance flexible thermally conductive insulating films that meet exacting standards for mass production without compromise.
FAQs about Flexible Thermally Conductive Insulating Film
How does a high thermal conductivity value transform electronic performance?It carries heat away from integrated circuit packaging, LED thermal management modules, and power electronic components almost like an invisible river running through the device.
- Keeps operation temperatures calm and steady.
- Guards microchips and boards against early burnout.
- Protects consistency in fast-moving high-performance computing devices.
Why is mechanical strength essential for flexible designs?
Within bending battery packs or vibrating drive units in electric cars, good mechanical strength property acts as the film’s backbone. The pairing of a dielectric polymer matrix with a flexible ceramic filler means:
- Survives seasonal humidity shifts without warping.
- Holds tight under assembly pressure and movement in service.
What shapes material choice during development?
Developers balance science with instinct, choosing fillers and resins that suit their design’s heartbeat. Key criteria often include:
| Specification | Importance |
| Defined dielectric strength standard | Safety for intricate circuits |
| Specific thermal resistance target | Matches cooling demand to size limits |
| Stable chemical resistance quality | Withstands long-term environmental stress |
How does controlled surface roughness lift energy efficiency?
A subtle texture across the thermally conductive polymer layer creates closer contact with metal casings.
- Drops interfacial resistance noticeably.
- Raises endurance against electrical breakdown when loads climb higher.
Which industries depend most on these films today?
From silent data center aisles to humming automotive plants, dependency runs deep:
- Electric vehicle battery pack manufacturers seeking compact safety layers.
- LED module producers aiming for cooler light output.
- IC packaging houses needing precision insulation in slim spaces.

 English
English
 usheenthermal
usheenthermal



