Everything You Need to Know About What is Thermal Pad Explained Simply
By now, you’ve probably heard the term tossed around — what is thermal pad — and thought, “Is this something I need to care about?” Oh yes. If your job involves sourcing materials for electronics that pump out heat like a summer sidewalk, then this squishy little square might just be your unsung hero. It’s not glamorous, but it could mean the difference between devices running cool or melting down mid-shift.And here’s the kicker—thermal pads don’t just transfer heat; they carry trust. Engineers stake their performance on them. Buyers stake their budgets on them. You’re not just buying material—you’re investing in operational uptime and brand reputation at scale. Keep reading—we’re about to unpack how these unassuming sheets pull some serious weight across industries big and small.
What Is Thermal Pad? An Easy Overview
Let’s break down what a thermal pad really is and why it matters for heat management in electronics.The science behind thermal conductivity performance
Understanding thermal conductivity starts with how heat flows through materials. A thermal pad acts like a bridge, moving heat away from hot components like CPUs or GPUs to cooler areas like heatsinks.- Heat transfers via phonons, tiny vibrations that carry energy through solid materials.
- Higher heat flux means faster transfer—ideal for high-performance electronics.
- Materials with low thermal resistance and low thermal impedance allow better flow.
- Think of it like this: the lower the resistance, the easier it is for heat to escape.
Types of thermal pads: Silicone vs Non-silicone thermal pads
Thermal interface materials come in two big families—each with its own perks depending on the job:Silicone Thermal Pads

- Made from flexible elastomeric pads, ideal for uneven surfaces
- Filled with conductive particles like metal oxides or ceramics
- Great conformability and long-term reliability
- Often used in consumer electronics due to their adaptability
- Typically use an acrylic or urethane-based polymer matrix
- Lower outgassing—important in optical or aerospace gear
- Less likely to cause contamination compared to silicone variants
- Preferred when sensitive environments demand ultra-clean operation
Key specifications: Dimension stability parameters and thickness tolerance
When selecting a good pad, don’t just chase high numbers on spec sheets. Pay close attention to these core traits:Dimensional Stability
- Keeps shape under pressure and temperature changes
- Prevents shifting that could affect contact area over time
- Impacts how well the pad fills gaps between surfaces
- Tighter tolerances = more consistent performance across devices
- Compression deflection defines how much force is needed to flatten the pad during installation.
- Shore hardness tells you how stiff or soft the material feels—a key factor in conformability.
- Manufacturing precision ensures repeatable quality batch after batch.
And now you know exactly what’s going on inside when someone asks, “Hey, what is thermal pad?”
The Importance of Thermal Pads in Electronics
Thermal pads are the unsung heroes behind cooler, longer-lasting electronics. Let’s unpack how they keep things chill under pressure.Ensuring efficient GPU thermal management
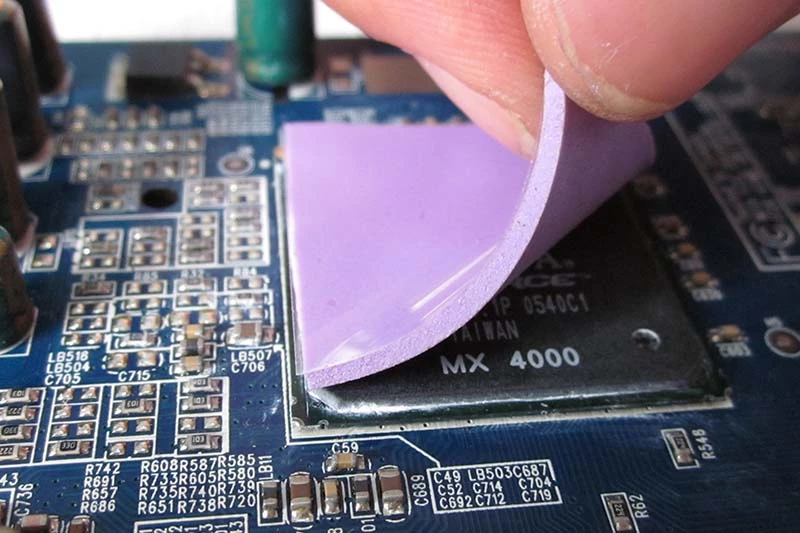
Keeping your GPU cool isn't just about fans—thermal pads play a major role too. Here's how they pull their weight:
- They fill microscopic air gaps between the GPU and heatsink, boosting heat dissipation.
- Their soft texture molds to uneven surfaces, improving thermal management without extra pressure.
- Unlike pastes, they’re mess-free and reusable during upgrades or repairs.
Long-term reliability assessment: Why it matters
Reliability isn’t just about surviving today—it’s about lasting through years of wear and tear. Here’s how engineers test for that:Step 1: Simulate extreme conditions with repeated thermal cycling, exposing materials to rapid temperature changes.
Step 2: Measure degradation over time—loss in thermal conductivity, cracking, or hardening signal failure risk.
Step 3: Evaluate lifespan predictions using stress data models to forecast real-world durability.
When users search “what is thermal pad” longevity like compared to paste? Pads often outlast standard greases, especially under frequent heating/cooling cycles common in mobile workstations.
Common Applications for Thermal Pads in Industries
Thermal pads are everywhere—quietly keeping our gadgets cool and steady. Here's how they shine in real-world tech.Power electronics cooling applications
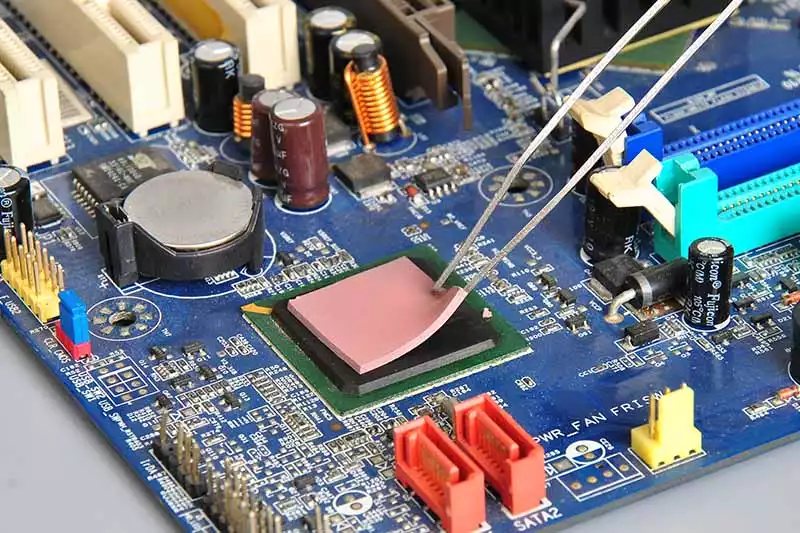
In power-hungry systems, heat buildup is no joke. Thermal pads step in where airflow alone just won’t cut it:
- Power modules like converters and inverters rely on thermal pads to push heat into the heat sink, keeping circuits stable.
- High-power switches such as IGBTs and MOSFETs generate serious heat during switching—pads help manage this without compromising performance.
- They provide essential electrical isolation, ensuring that current doesn't arc between components while still letting heat flow out.
- By lowering thermal resistance, they help reduce junction temperatures, which directly boosts component reliability over time.
- In compact designs, pads fill microscopic gaps, improving contact between surfaces and maximizing heat transfer efficiency.
Automotive electronics thermal management

Modern vehicles are rolling computers—and every ECU or sensor needs a way to chill out under the hood.
- In ECUs, especially those tied to engine control or transmission systems, thermal pads prevent overheating during long drives or traffic jams.
- For systems like ADAS, where real-time processing is critical, stable temperatures mean better accuracy and faster response times.
- Inside infotainment units, these pads keep processors from throttling when you're streaming music or using navigation apps for hours on end.
According to Yole Group’s 2024 report on automotive thermal interface materials: "The global demand for high-performance TIMs has grown by over 22% year-on-year due to increased electronic density in EV platforms." So next time someone asks what is a thermal pad used for? Tell them—it’s
what keeps your car's brain from frying.
LED lighting cooling solutions
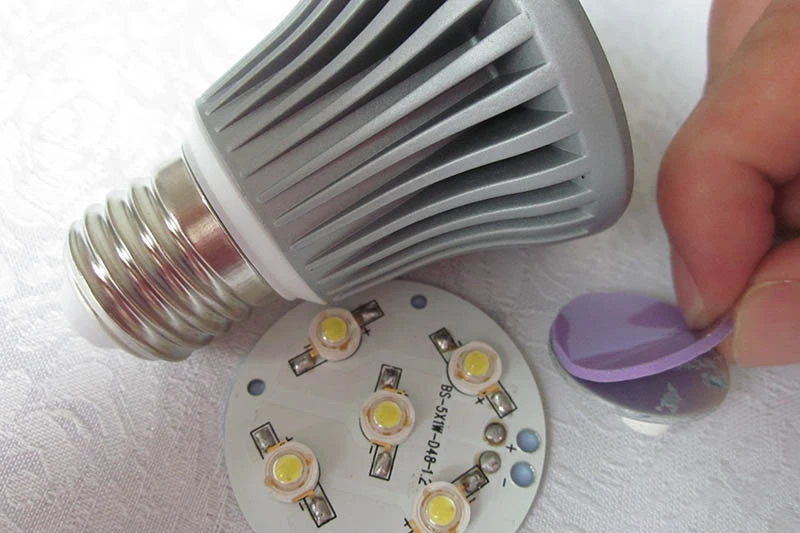

LEDs may look simple on the outside—but inside? It’s all about managing that tiny but intense hotspot at the core.
Each LED has a delicate little heart called the LED junction, where light is born—and so is heat. If you don’t pull that heat away fast enough?
- You lose brightness over time (lumen maintenance).
- The whole fixture dies young (lifespan).
- Your energy savings go up in smoke.
They’re also key players behind sleek downlights and smart bulbs with tight spaces—because good cooling helps support more compact designs without burning things out too soon.
So yeah… if you've been scratching your head asking “what is thermal pad” doing inside your smart lamp? It's working overtime so your light doesn’t fade before its time.
Choosing the Right Thermal Pad for Your Needs
Quick tip: Picking a thermal pad isn’t just about thickness—it’s about material properties, pressure, and how hot things get under the hood.Factors to consider: Hardness Shore A durometer and operating temperature range
- When choosing a thermal pad, don’t skip checking the Hardness rating—measured on the Shore A durometer scale. Lower numbers mean squishier pads, which can fill in tighter gaps better.
- The operating temperature range is crucial too. If your device runs hot, you need a pad with excellent thermal stability that won’t break down over time.
- Materials like silicone and graphite have different sweet spots for both heat resistance and firmness—match them to your use case.
Understanding compression rate characteristics in thermal pads
- Compression rate affects how well a pad conforms to uneven surfaces—this determines how much heat actually gets transferred.
- Higher compression means better gap filling, but too much can lead to material fatigue or breakage over time due to excess pressure buildup.
- Pay attention to how the pad behaves under load; some materials offer better long-term deflection without losing shape.
Process optimization: Die-cutting and adhesive application techniques
- Precision matters when it comes to cutting pads for electronics assembly—automated die-cutting ensures clean edges that fit perfectly every time.
- Adding adhesive? Go for high-tack options that bond securely without gumming up components during placement or rework.
Customization tips based on application needs
→ For laptops or small form-factor PCs, go with low-force, high-conformability materials that fill micro-gaps without stressing delicate parts.→ In automotive ECUs or power converters, choose high-temperature rated compounds with stronger structural integrity.
→ For prototyping environments, modular sheets with easy-to-peel liners make quick swaps possible without damaging circuits.
Impact of Low-Quality Thermal Pads on Device Performance
Cheap thermal pads might save a few bucks upfront, but the hit they deliver to performance and safety? That cost runs deep.The risks of inadequate thermal resistance measurement
When someone asks, what is thermal pad, they’re usually trying to figure out how it helps with heat management. But if the thermal resistance isn’t measured right, things can get messy fast.- Inconsistent measurement accuracy leads to unpredictable results—your CPU might run cool one day and toast the next.
- A pad with poor thermal conductivity won’t transfer heat efficiently, causing internal components to cook under pressure.
- Bad test setups or flawed test methodology skew data, hiding real issues until it's too late.
Consequences of poor performance: Electrical insulation capability and breakdown voltage withstand
Let’s break this down into bite-sized reality checks—because when a thermal pad fails electrically, it’s not just inconvenient—it’s dangerous.- Poor electrical insulation means current might leak where it shouldn’t.
- Weak dielectric strength opens the door to arcing and shorts.
- Low-grade materials degrade over time, especially under high temps.
- Once your system faces a drop in breakdown voltage, you're flirting with total failure.
And if you're still wondering what is thermal pad used for beyond cooling—it's also there to keep electricity in its lane. Don’t let bad insulation turn your gear into a hazard.
FAQs about What Is Thermal Pad
1. What is a thermal pad and how does it function in heat transfer?A thermal pad bridges the gap between electronic components and their heatsink, guiding excess heat away to keep systems stable.
· Core materials include Silicone thermal pad, Graphite thermal pad, and Ceramic thermal pad, each chosen by engineers for specific balance between flexibility, conductivity, and insulation.
· With the help of fine-tuned thickness tolerance requirements and thermal resistance measurement, pads ensure components like chips on GPUs or LED modules maintain proper cooling contact.
In practice—its quiet task: absorbing micro-level surface irregularities so that temperature builds no longer threaten circuits.
2. How do material types affect performance across devices?
The choice of material determines both texture under compression and endurance under high workload conditions.
| Material Type | Common Application | Distinct Advantage |
| Silicone Thermal Pad | Laptop heat dissipation & GPU cooling | Flexible fit; stable across wide operating temperature range |
| Graphite Thermal Pad | Power electronics cooling & automotive electronics thermal areas | Fast lateral spreading; low thickness requirement |
| Non-silicone Thermal Pad | LED lighting or optics modules requiring halogen-free material verification | Clean finish; low outgassing behavior |
Each type undergoes testing with a thermal conductivity tester machine to confirm promised efficiency before entering full-scale production lines.
3. Which specifications define high-quality thermally conductive materials?
Fine mechanical traits play as important a role as chemical content:
① Balanced compression rate characteristics prevent mechanical stress during assembly pressure cycles measured by the compression testing apparatus.
② Controlled Hardness Shore A durometer gives consistent surface conformity without tearing edges during lamination stages.
③ Stable geometry maintained through strict dimension stability parameters, ensuring uniform pressure after die-cutting process optimization is executed by manufacturers.
The reward—long-term reliability assessment results that prove integrity remains even when environmental simulation chamber trials push temperatures toward limits.
4. Why does standard compliance matter in large-scale sourcing?
Beyond cost negotiations lies credibility built through verified documents:
★ RoHS compliance certification, proof against hazardous elements harming users or recyclers alike.
★ UL flammability rating, safeguarding assemblies inside confined laptop chassis where current peaks can ignite untested polymers.
★ Adherence to REACH regulation adherence ensures global acceptance in multinational OEM supply chains governed by eco-audits.
Once combined with disciplined process control—from adhesive application technique precision to curing process optimization—the result feels almost human: predictably reliable yet adaptable under real-world heating rhythms every device faces daily.

 English
English
 usheenthermal
usheenthermal



