How to Decide Between Thermal Pads vs Thermal Paste for Optimal Cooling
When it comes to cooling down electronics, the debate about thermal pads VS thermal paste has never ceased,thousands of engineers and procurement leads are sweating bullets trying to balance cost efficiency with long-term performance.

Truth is, picking between the two isn’t some black-and-white decision—it depends on how much heat you’re pushing and how scalable your process needs to be. And when Sheen Electronic Technology’s senior engineer said in their 2025 Q2 report that “material choice impacts not just cooling but yield rate across assembly lines,” we knew this wasn’t a niche issue anymore—it’s business-critical.
Thermal Pads vs Thermal Paste: Core Differences Explained
This guide breaks down the key contrasts between thermal pads and thermal paste—helping you choose the right cooling solution for your PC build or upgrade.Understanding Thermal Interface Materials: Pads and Paste Compared
.webp)
.webp)
- Thermal pads are semi-solid sheets made to bridge gaps between chips and heatsinks.
- Thermal paste, on the other hand, is a gooey compound that fills microscopic surface imperfections.
Key Attributes: Thermal Paste vs Phase Change Material

Silicone Thermal Paste offers reliable results over time but takes finesse during application.
Phase Change Material, though more forgiving at first touch, needs heat cycles to kick into full performance mode.
Which one wins? Depends on whether you're after plug-and-play ease or long-haul consistency.
Usage Scenarios: CPU Heat Dissipation and GPU Thermal Management
- CPUs with tight tolerances benefit most from precise application of thermal paste, especially high-performance builds needing max heat transfer.
- GPUs often have wider contact areas; some OEMs even use thick thermal pads for VRAM modules and power delivery zones.
When Should You Replace Your TIM?
- If your system temps spike without hardware changes—it’s time to check that TIM layer.
- After removing a heatsink—even just once—you should reapply new thermal paste or replace old pads.
- Every couple years on older rigs helps maintain optimal cooling performance.
Common Mistakes When Applying Thermal Solutions
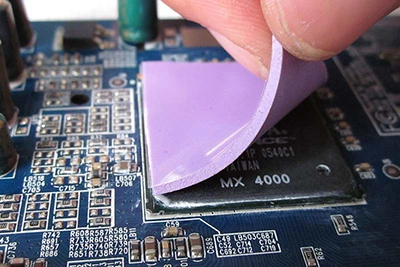

- Don’t overdo it—too much paste insulates instead of cooling.
- Never reuse old thermal pads—they lose elasticity and effectiveness fast.
- Avoid mixing materials; combining pad residue with fresh Paste is a recipe for disaster.
- Clean both surfaces thoroughly before applying anything new.
Choosing Between Pad and Paste Based on Device Type
- Laptops — Usually favor thin factory-installed thermal pads, but upgrading with quality paste can reduce throttling significantly if done right.
- Desktops — Custom builds thrive on high-grade thermal Paste , especially for unlocked CPUs under heavy load.
- Consoles — Often rely on thick pre-cut pads, but modders sometimes swap them out for better pastes around APU cores for improved airflow balance.
Thermal Conductivity: Heat Transfer Performance of Pads and Paste
Getting the best heat transfer? It’s all about choosing right between thermal pads and thermal paste.Measuring Thermal Conductivity Performance: Testing Methods & Standards
When it comes to comparing thermal paste vs thermal pads, standardized testing is the only way to separate guesswork from real data. Here’s how it’s done:- ASTM D5470 is the gold standard for measuring thermal resistance under pressure.
- Other common standards include ISO 22007 and ASTM E1530, especially when dealing with thin-film materials.
- Lab setups simulate real-world mounting pressures, making results more relevant for electronics.
- Test results are usually expressed in watts per meter-kelvin (W/m·K)—higher is better.
The Role of Viscosity and Consistency in Heat Transfer
Viscosity isn’t just a fancy ter, it decides how your material behaves under pressure. For example:- A thick thermal paste might resist spreading, but fills micro gaps better than rigid pads.
- Low-viscosity pastes can be messy but are easier to apply evenly across CPUs or GPUs.
Comparing Electrical Insulation Capability in Thermal Solutions
Let’s talk safety—not just heat flow. Some applications need electrical isolation as much as thermal conductivity.If you're working near sensitive circuits, go pad-heavy—especially if your heatsink might shift or vibrate during operation.
How Operating Temperature Range Affects Material Performance
- Thermal pastes, especially those loaded with metal oxides or ceramics, handle extreme temps above 150°C without breaking down.
- But they can dry out over time if exposed too long at peak loads.
- In contrast, most thermal interface pads maintain integrity between –40°C to +125°C—ideal for moderate environments like laptops or embedded boards.
- High-temp silicone variants exist but often sacrifice flexibility or insulation quality.
- Choosing wrong means degraded performance over time—even if things seem fine at first boot-up.
Long-Term Stability: Thermal Pads vs Thermal Paste
Thermal interface materials age differently. Let’s unpack how each holds up under pressure, time, and heat.Long-Term Stability Reliability: What to Expect from Each Material
When comparing thermal pads vs thermal paste, durability is where things get interesting:Thermal Pads
- Hold their shape over time with minimal degradation.
- Offer steady conductivity across years of use.
- Less prone to air gaps forming due to hardening or shrinkage.
- Often rated for long-term reliability in industrial environments.
- Can dry out depending on ambient temperature and humidity.
- May require reapplication every few years—especially under heavy loads.
- Some high-end pastes retain performance better but still face gradual decline.
- Susceptible to pump-out effect, reducing effective surface contact.
Curing Process Impacts: The Importance of Quality Inspection Protocols
Not all thermal compounds are ready right out of the tube—or pad.- Some phase-change materials need a heat cycle to fully activate their bonding properties. This “curing” process ensures optimal surface adhesion and fills microscopic voids between surfaces.
- Without proper manufacturing oversight, inconsistencies like uneven thickness or trapped air can cause early failures. That’s why rigorous inspection protocols during production matter more than most realize.
Storage and Handling Guidelines for Optimal Longevity
Step 1 – Store thermal paste in an airtight container at room temperature (ideally below 25°C). Exposure to oxygen leads to premature drying and loss of viscosity.Step 2 – Keep away from direct sunlight or fluctuating humidity levels; both can mess with chemical stability over time.
Step 3 – For thermal pads? Way easier. Just avoid folding them sharply or exposing them to dust before installation—they’re much less sensitive overall when it comes to storage conditions.
In short, when comparing thermal pads vs thermal paste in terms of shelf life and ease-of-use before deployment, pads are practically foolproof while pastes need babysitting if you're planning on keeping them around awhile.
Cost Analysis: Thermal Pads vs Thermal Paste at Scale
Understanding the price-performance tradeoffs in large-scale cooling solutions helps teams make smarter procurement calls.Bulk Packaging Solutions: Evaluating Cost-Effectiveness
When you're buying thermal interface materials in bulk, every cent counts—and packaging plays a bigger role than you'd think.Storage Efficiency & Format Variety
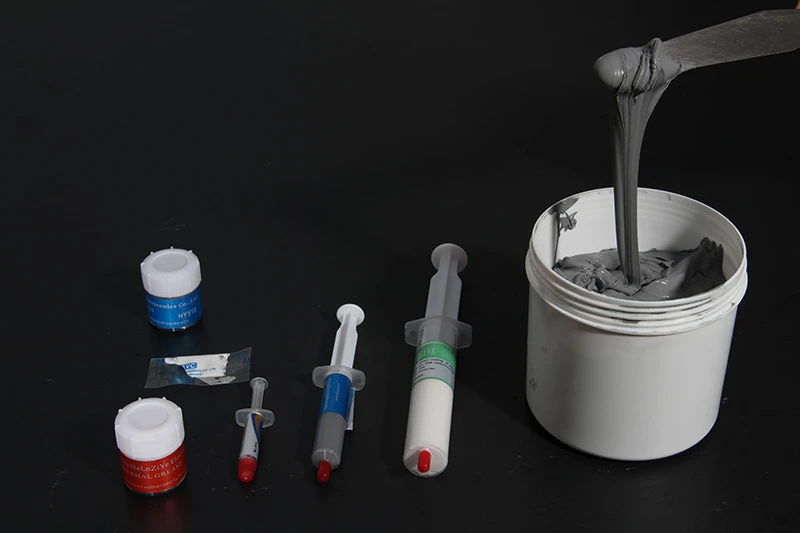
- Thermal paste often comes in jars, syringes, or industrial cartridges, each offering different cost-per-use ratios.
- Thermal pads, on the other hand, are usually pre-cut and stacked—less mess but less flexible sizing.
- Bulk paste containers reduce individual packaging waste but may require skilled application tools.
- Pre-sized pads minimize trimming time and errors during installation.
- Paste in bulk weighs less per gram of usable material due to minimal packaging overhead.
- Pads can be heavier and more rigidly packed, increasing freight volume costs over time.
Custom Packaging Requirements: What Matters for Large Purchases
Big orders don’t just need more product—they need smarter delivery formats that scale with production needs.- Want clean application? Syringe-style dispensers with precision tips help avoid overuse.
- Need speed? Stencil-based paste deployment reduces human error and boosts throughput.
- Prefer zero waste? Go for pre-cut thermal pads tailored to your device specs—no trimming needed.
- Concerned about shelf life? Vacuum-sealed cartridges preserve thermal paste longer under factory conditions.
FAQs about Thermal Pads vs Thermal Paste
1. How are thermal pads and thermal paste used differently in CPU or GPU cooling?· Thermal Pads – solid, ready-cut sheets that bridge uneven gaps; suited to GPU thermal management, larger spreads, or spaces where quick application replaces delicate handiwork.
· Thermal Paste – a pliable thermal interface material spread with care through a precise application method, perfect for finely honed CPU surfaces needing intimate contact for peak thermal conductivity performance.
2. Which has better long-term reliability under constant operation?
· Conductive silicone grease (paste) can dry with age unless stored following strict storage and handling guidelines, often in sealed syringe packaging options.
· Phase change materials and pads tend to hold form longer—resisting creep during years of service in power amplifier cooling or LED setups where reapplication is undesirable.
3. Why does viscosity matter when ordering large batches?
· For automated dispensing systems or stencil application machines, consistent viscosity keeps distribution even across thousands of units per shift.
· High-viscosity pastes hug microscopic grooves—a trait prized by those fine-tuning CPU heat dissipation, while pads arrive already “fixed” in thickness but lack fluid adaptability on micro scales.
4. How should operating temperature range guide choice at scale?
A clear branch line separates uses: wide-range paste formulations endure extreme cycling—think heavy-load GPUs bouncing between hot benchmarks and idle cool-downs—while fixed-form pads excel within moderate windows like steady LED lighting panels or modest semiconductor device cooling projects.
5. Why consider electrical insulation features when buying thousands of units?
· Halogen-free insulating pads shield against shorts while managing heat on tight boards.
· Pastes vary; certain formulas lack inherent insulation, requiring an added epoxy bonding adhesive barrier if brushing close to live traces during assembly near high-voltage paths.

 English
English
 usheenthermal
usheenthermal



