What Is the Best Thermal Glue—and How Do You Choose the Right One?
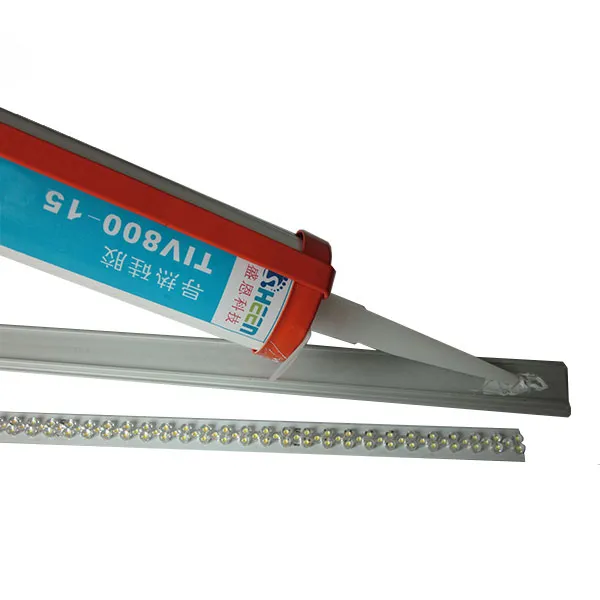

Research by Sheen Technology has revealed that with the continuous development of fields such as artificial intelligence, electric vehicles, and communication equipment, thermally glue, as a thermal interface material, have transformed from a convenience requirement to a critical need, playing a decisive role in application structures.
Comparison of Thermal Glue Types: Epoxy, Silicone, and Acrylic Resins
Selecting the optimal thermal glue requires understanding its types and chemical composition, as different types possess distinct structural characteristics.
- Epoxy Thermal glue
Advantages: Exceptionally high shear strength, high thermal conductivity, and flame-retardant properties.
Disadvantages: Highly brittle.
Best Use: Structural bonding of large, heavy aluminum heat sinks.
- Silicone-Based Thermal glue
Advantages: Exceptional flexibility.
Disadvantages: Requires extended curing time, with natural curing taking up to 24 hours.
Best applications: LED lighting assemblies, automotive electronics, and high-vibration environments.
- Cyanoacrylates and Acrylates
Advantages: Rapid curing saves time and suits automation.
Disadvantages: Lowest thermal conductivity; unsuitable for high-power components.
Best uses: Temporary bonding and rapid prototyping.
| Metric | Silicone | Thermal Epoxy | Acrylic |
| Shear Strength (psi) | Moderate (200–800) | Very High (>2000) | High (Varies widely) |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Moderate to High (Up to 2.5 W/mK) | High (Up to 4 W/mK) | Low to Moderate |
| Flexibility / Stress Relief | High (Flexible) | Low (Rigid) | Low (Rigid) |
| Cure Time | Slow (4–24 Hours) | Fast (Minutes/Hours) | Very Fast (Seconds/Minutes) |
How to Select the Best Thermal Glue for Applications
Selecting the ideal thermal glue involves more than just focusing on parameters like thermal conductivity; it requires a multifaceted engineering assessment of solution feasibility. For example:
- Thermal Conductivity and Bonded Layer Thickness (BLT)
- Electrical Insulation
- Predicting Thermal glue Failure Risks
- Operating Temperature
Thermal glue Use Cases: LEDs, GPUs, and Heavy Heat Sinks
Optimal Thermal glue for LEDs and Lighting Equipment
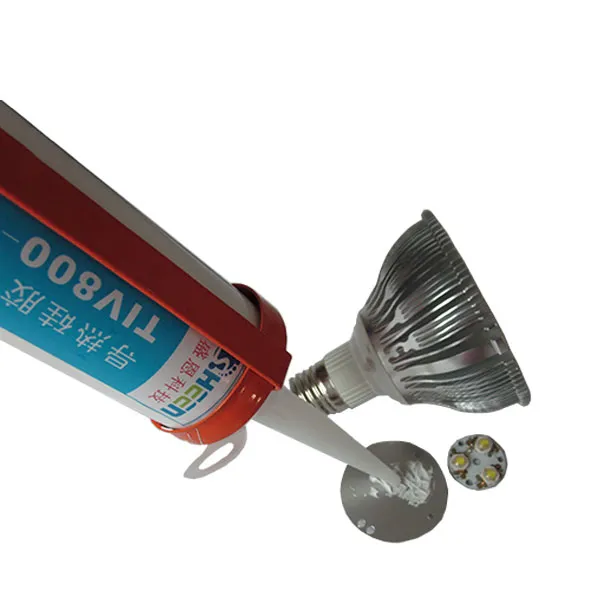

- Recommended Solution: Single-component curing thermal glue.
- Reason: LEDs are highly sensitive to the high internal stress of rigid epoxy resins, which may cause color shift or premature failure. The flexibility of silicone adapts to the continuous thermal expansion of aluminum backplanes, while its neutral curing formula prevents copper trace corrosion.
- Recommended: Epoxy thermal glue.
- Reason: Epoxy provides the necessary structural load-bearing capacity for heavy components.
- Recommended Solution: Thermal tape or low-strength silicone.
- Reason: Considering rework requirements, using high-strength epoxy may damage expensive graphics cards when removing heatsinks for future maintenance or upgrades.
Q:Are thermal glue and thermal conductive paste the same thermally conductive material?
A:No. Although both thermal conductive paste and thermal glue are thermal interface materials, thermal conductive paste lacks adhesive strength, and their product functions differ. Thermal glue possesses both thermal conductivity and adhesive properties, and can be used to fix components.
Q:How long does thermal glue take to cure?
A:Curing time is divided into surface drying time and natural curing time, which vary depending on the thermal glue material. For example, single-component thermal glue can take up to 24 hours to cure naturally.
Q:Can I use super glue instead of thermal conductive adhesive?
A:This depends on the application requirements. Generally, super glue cannot be used as a substitute for thermal conductive adhesive in typical applications.
Q:How to separate epoxy resin thermal glue from a heat sink?
A:Epoxy resin thermal glue is a permanent structural adhesive, making rework difficult, so this is very challenging.
The only commonly used method is thermal cycling, which causes the brittle epoxy resin to shrink, making it more susceptible to shear forces. Even using this method, separation is not guaranteed, and precision electronic components may still be damaged. If future maintenance is anticipated, avoid using permanent epoxy resin whenever possible.
The selection of the optimal thermal glue does not rely on a single highest parameter, but rather on whether the adhesive can maintain structural stability and thermal performance integrity within the specific application context.
If you require a reliable permanent solution? Contact our engineering team for customized thermal design consultation. Sheen Technology will provide you with professional and comprehensive thermal management solutions.

 English
English
 usheenthermal
usheenthermal



