Thermal conductivity paste applied in PCB, heat sink, LED lamp, etc
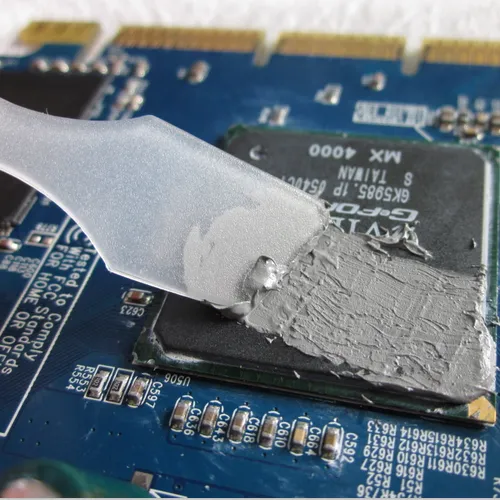
Thermal conductivity paste is used in PCBs to fill tiny gaps between heat-generating components (such as integrated circuits) and heat spreaders or heat sinks. Its paste-like texture allows it to conform to micro-irregularities on surfaces, ensuring maximum contact for efficient heat transfer. This helps prevent heat buildup in dense PCB layouts, maintaining component performance and longevity. It’s easy to apply in small quantities, making it suitable for precise, space-constrained PCB assemblies.
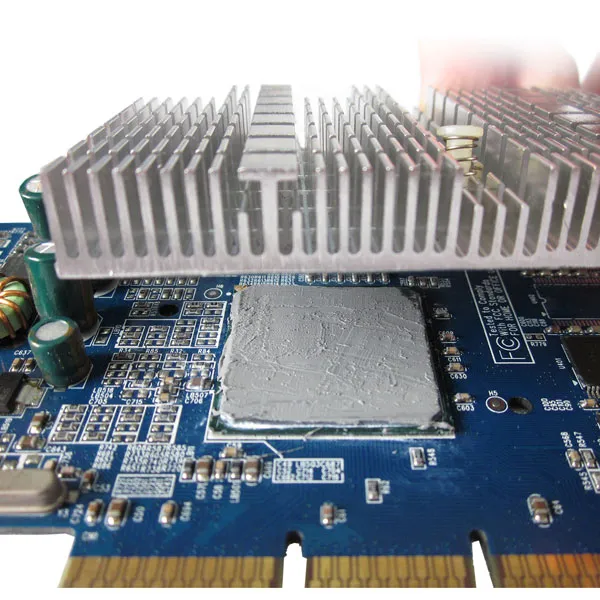
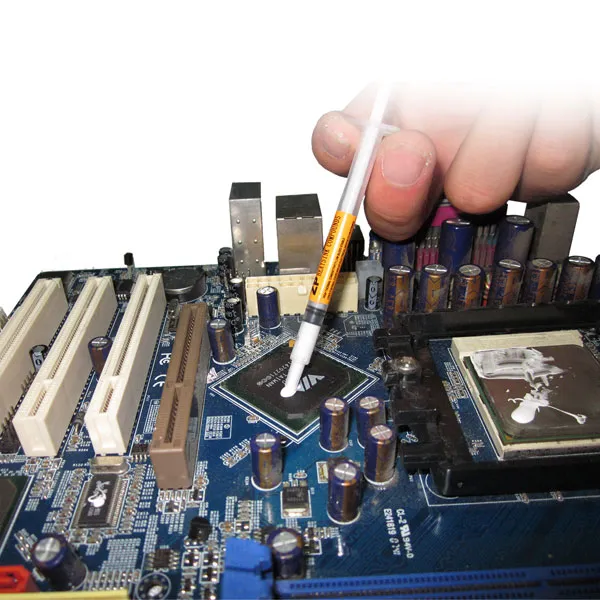


For heat sinks, thermal conductivity paste serves as a critical interface between the heat sink and heat sources like CPUs or power modules. It eliminates air pockets between the two surfaces, which are poor heat conductors, thus reducing thermal resistance. The paste spreads evenly under pressure, creating a thin, continuous layer that facilitates rapid heat transfer from the source to the heat sink. This ensures the heat sink can effectively dissipate heat, keeping components within safe operating temperatures.
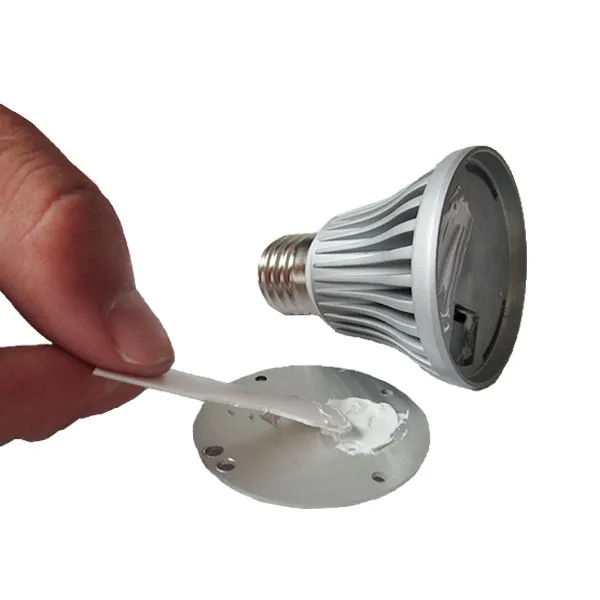


In LED lamps, thermal conductivity paste is applied between LEDs and their heat sinks to manage the significant heat produced by LEDs. It forms a low-resistance thermal path, allowing heat to flow efficiently from the LED chip to the heat sink. This prevents overheating, which can dim LED brightness and shorten lifespan. The paste’s ability to adapt to surface variations ensures consistent thermal contact over time, even with thermal cycling, maintaining reliable lamp performance.

 English
English
 usheenthermal
usheenthermal



