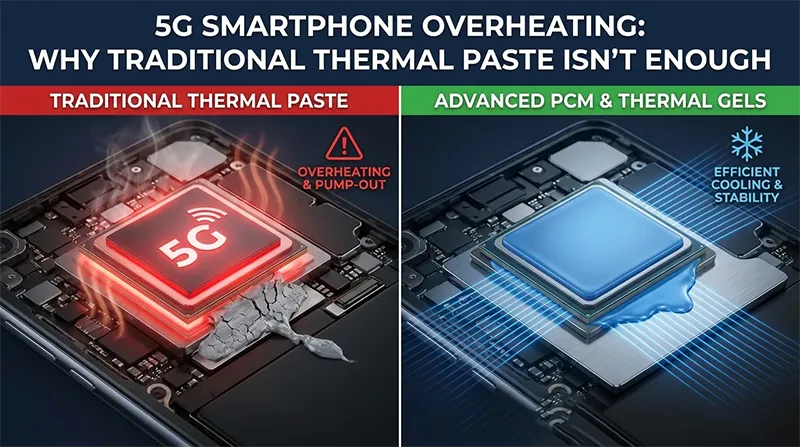
5G Smartphone Overheating Solutions: Why Traditional Thermal Paste Isn't Enough?
The issue of smartphone overheating is increasingly troubling modern users. New 5G flagship models become too hot to hold after just ten minutes of intensive gaming or large file downloads. Furthermore, the continuous advancement of smartphone performance—combined with 120Hz high-refresh-rate displays and complex multi-lens camera arrays—poses significant thermal challenges for 5G devices.Traditionally, thermal paste has been the most common thermal interface material connecting chips to heat sinks. However, this material struggles to meet the high power density and performance demands of modern mobile devices. To maintain performance and prevent throttling, the industry is shifting toward advanced phase-change materials and thermal gels—currently the most reliable solutions.
The Physics of 5G Heat: Why mmWave Modems Break Traditional Cooling
Processing Gigabit data speeds creates an exponential increase in heat compared to 4G LTE. The power penalty of 5G is most evident in mmWave thermal challenges. Unlike internal SoCs (System on a Chip), these antennas are often located at the device’s edge—precisely where a user’s hand grips the phone. This requires a cooling strategy focused on rapid heat spreading rather than just simple dissipation to prevent local "hot spots".- The Power Penalty of High-Speed Data: Gigabit processing generates significant thermal energy, particularly within mmWave antenna modules.
- The challenge of extreme space constraints: Modern smartphones often measure less than 8 millimeters thick, demanding thermal interface materials (TIM) that are ultra-thin (typically under 0.2 millimeters) and possess exceptional thermal conductivity.
- Thermal throttling impacts performance: When device contact temperatures persistently rise, if the thermal interface material fails to efficiently dissipate heat in a timely manner, the device will immediately throttle its performance to protect both the device and user safety.
The Failure Mode: Why Traditional Thermal Paste "Pumps Out" in Mobiles?
The primary reason traditional thermal paste fails in mobile environments is the thermal paste pump-out effect.- Understanding Pump-Out: Traditional thermal paste possesses low thermal resistance and excellent wetting properties. However, under continuous high-pressure expansion and contraction, the paste is squeezed out, causing it to detach from the interface.
- Gap Formation: Once the thermal paste is extruded, an air gap forms between the chip and the heat sink, leading to a sudden temperature spike.
- Drying Risk: Prolonged high-temperature operation evaporates solvents in low-cost thermal compounds, transforming the material into a cracked, powdery insulator.
- Long-Term Impact: This degradation typically manifests within 6 to 12 months, causing performance degradation and increasing warranty repair rates.
Sheen’s Advanced Solutions: Phase Change Materials (PCM) and Thermal Gels
To combat 5G smartphone overheating, Sheen Tech has developed the SE and SP Series. These phase change materials are solid at room temperature for easy handling but turn into a high-performance liquid at operating temperatures to achieve ultra-low thermal resistance.
| Model | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
Thermal Impedance (℃*in²/W)@30psi |
Normal Thickness (mm) |
Customized Thickness (mm) |
Density (g/cm³) |
Dielectric Constant (1MHz) |
Phase Change Temp (℃) |
Operating Temp (℃) |
| SP205A-30 | 3.0 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 0.13~0.5 | 2.85 | 3.0 | 45~55 | -40~125 |
| SP205A-35 | 3.5 | 0.04 | 0.2 | 0.13~0.5 | 2.75 | 3.0 | 45~55 | -40~125 |
| SP205A-40 | 4.0 | 0.03 | 0.2 | 0.2~0.5 | 2.75 | 4.0 | 45~55 | -40~125 |
| SP205A-50 | 5.0 | 0.02 | 0.3 | 0.2~0.5 | 2.9 | 4.0 | 45~55 | -40~125 |
| SP205A-60 | 6.0 | 0.015 | 0.3 | 0.2~0.5 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 45~55 | -40~125 |
| SP205A-L-80 | 8.0 | 0.007 | 0.3 | 0.2~0.5 | 2.8 | 3.1 | 45~55 | -20~100 |
| SP350P | 1.8 | 0.4 | 0.13~0.5 | 0.13~0.5 | - | 4.5 | 45~55 | -40~125 |
PCM Reliability: PCM is inherently resistant to pump-out because it re-solidifies every time the phone cools, "healing" any gaps that may have formed during use.
Case Study: A major Android OEM recently reduced thermal throttling by 15% in their flagship model by switching from traditional grease to Sheen’s PCM.

| Model | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
Thermal Impedance (℃*in²/W) @30psi |
Density (g/cm³) |
Outgassing | Flow Rate (g/min) @30cc,90psi |
Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) |
| SE20 | 2.0 | 0.10 | 2.5 | <0.5% | 80±15 | 2.5 |
| SE30 | 3.0 | 0.08 | 3.0 | <0.5% | 25±15 | 5.5 |
| SE35 | 3.5 | 0.065 | 3.0 | <0.5% | 30±15 | 5.5 |
| SE40 | 4.0 | 0.06 | 3.1 | <0.5% | 40±15 | 7.0 |
| SE50 | 5.0 | 0.06 | 3.1 | <0.5% | 40±15 | 7.0 |
| SE60 | 6.0 | 0.045 | 3.3 | <0.5% | 20±15 | 8.0 |
| SE80 | 8.0 | 0.05 | 3.4 | <0.5% | 30±15 | 8.0 |
| SE100 | 10.0 | 0.045 | 3.4 | <0.5% | 10±15 | 8.0 |
One-Component Thermal Gels: Designed for automated dispensing, these high-flow gels are ideal for complex EMI shields and uneven surfaces where a flat pad cannot make consistent contact.
Carbon Fiber Sheets: Sheen also utilizes high-conductivity carbon fiber solutions to spread heat away from the 5G antenna toward the rest of the chassis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why does my phone get hot when using 5G?5G modems, especially when using mmWave frequencies, require significantly more power to process high-speed data, generating more heat than 4G modems.
Is thermal paste or a thermal pad better for phones?
Neither is ideal for 5G; PCM or Thermal Gels are superior because they provide the low resistance of a paste with the long-term stability of a pad.
Can thermal paste dry out inside a phone?
Yes, high heat density can cause the solvents in standard pastes to evaporate, leading to cracked, ineffective insulation.
What is the thinnest thermal interface gap?
Thermal paste and thermal gel enable bonded layer thicknesses as low as 0.02mm, delivering the lowest thermal resistance in space-constrained designs.
In the 5G era, traditional thermal pastes can no longer meet the high power density and mechanical stress demands of modern flagship devices. To prevent performance throttling and hardware degradation, manufacturers must adopt materials specifically engineered for mobile use cases.
Sheen Technology adheres to an “application-solution-oriented” philosophy, ensuring effective solutions to the pumping-out and drying-out issues plaguing 5G hardware. Is your device struggling with 5G thermal loads? Contact us immediately for samples of our thermal interface material series and professional thermal management solutions.

 English
English
 usheenthermal
usheenthermal



